By using the BoreCam™ on a regular basis to scope holes and plot measurements, you can predict when roof failure is imminent in the measured roof areas. This information allows you to take preventive action to better increase underground safety.

Roof fall in a limestone mine.
The BoreCam™, when properly used, is a valuable tool in numerous ways because it allows you to see into the rock of the roof or pillar. The information allows you to assess the geological conditions and stress failures in the roof rock as a significant part of evaluating the stability of the roof. This is a valuable tool for examining the roof rock in areas of higher exposure to mining personnel in locations such as underground shops, warehouses, offices, lunchrooms, other gathering places, and travelways. If The BoreCam™ results indicate possible issues with the roof beam, roof monitors can be installed to measure the stability.

Scoping roof holes in a salt mine.
The BoreCam™ is an indispensable tool in the rock mechanics engineer’s information-gathering process. This technology allows the rock mechanics engineer to visually observe in real time the integrity of the rock in the roof beam. Roof holes are drilled and cleaned with water or brushes and the camera head is inserted in the hole using an insertion rod with distance marks. The camera can scope holes tens of meters long but are most commonly used in holes about 3 to 7 meters above the roof.
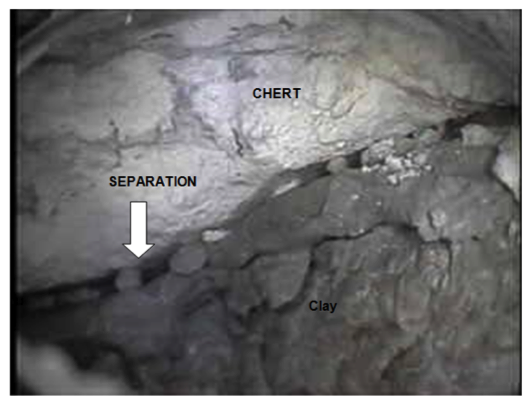
A view from the BoreCam™ showing a separation in the roof rock.
In addition to using The Borecam™ to gather data for the long-term analysis of ground stability, you can also use the camera to evaluate the geology and potential for stress failures at the mining face. By scoping roof holes near the mining face, you can gather data to determine whether or not the roof rock is favorable or unfavorable geology. In many cases, when a mine experiences an unexpected roof fall, it is because the geology in the roof changes as the face advances and the miners have been unaware of the change. The camera allows you to immediately recognize weaker geology in the roof rocks and appropriate corrective action can be taken; for example, adjusting the roof support system to accommodate for the new conditions.
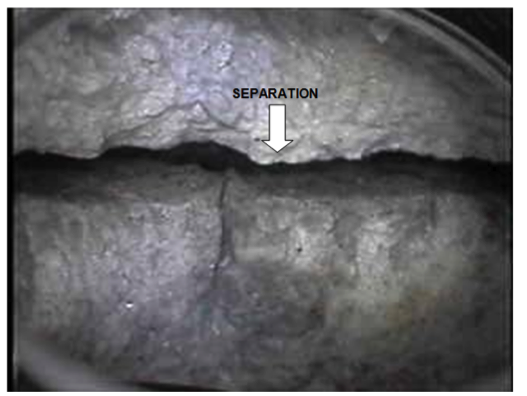
A view from the BoreCam™ showing a separation in the roof rock.
The BoreCam™ allows the engineer to efficiently view how the roof beam reacts to mine-induced stresses by scoping holes back from the advancing face where the pillars and roof beam come under full loading conditions. You can see if separations or fractures have developed in the roof beam along with their locations. If fractures or separations are found close to the mine roof, this is a cause for immediate concern and action, especially if the roof is not mechanically supported. Fractures or separations found higher up the borehole are especially a concern if they are above the bolt anchorage. Logging these locations is highly effective in assessing roof performance and stability and, therefore, in predicting and preventing roof falls.
For additional resources on mine safety visit: RockTec Solutions